Heartburn and indigestion are common digestive issues that can cause significant discomfort. Many people turn to milk as a home remedy, believing it can soothe the burning sensation and help with digestion. Dairy products, including milk, have long been touted for their health benefits, such as providing essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D.
However, their impact on digestive health is a bit more complex. While some research suggests that dairy can help neutralize stomach acid temporarily, other studies indicate that milk might actually stimulate acid production in the stomach, potentially worsening symptoms in the long run.
Understanding the true effects of milk on heartburn and indigestion requires a closer look at the science behind these claims.
What Causes Heartburn and Indigestion?
Heartburn and indigestion are often caused by a variety of factors, ranging from dietary habits to underlying medical conditions. Heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest, occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, irritating its lining.
Indigestion, or dyspepsia, refers to a general discomfort in the upper abdomen and can be accompanied by bloating, nausea, and belching. Understanding the root causes of these digestive issues can help in managing and preventing them effectively.
Dietary Choices: Spicy, fatty, or acidic foods and beverages can trigger heartburn and indigestion.
Overeating: Consuming large meals can increase pressure on the stomach, leading to acid reflux and discomfort.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress can contribute to digestive issues.
Medical Conditions: Conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and hiatal hernias can cause or exacerbate symptoms.
Medications: Certain medications, including anti-inflammatory drugs and aspirin, can irritate the stomach lining.
Eating Habits: Eating too quickly or lying down immediately after eating can lead to heartburn and indigestion.
Is Milk an Antacid?
Milk is often considered a natural remedy for heartburn due to its initial soothing effect. When you first drink milk, its cool, smooth texture can provide temporary relief by coating the esophagus and stomach lining, creating a barrier against stomach acid. This effect, however, is short-lived.
Milk contains calcium and protein, which can actually stimulate the stomach to produce more acid, potentially leading to a rebound effect where heartburn and indigestion symptoms return or even worsen.
Therefore, while milk might seem like an antacid at first, its overall impact on acid production suggests that it might not be the best long-term solution for managing heartburn and indigestion.
Which Milk Helps with Heartburn: Cold or Warm?
When considering whether cold or warm milk is more effective for alleviating heartburn, cold milk tends to be the preferred choice. Cold milk has a soothing effect on the inflamed lining of the esophagus and stomach, providing immediate relief from the burning sensation associated with heartburn.
The cool temperature helps to neutralize excess stomach acid temporarily and can create a protective layer over the stomach lining, reducing discomfort. However, it’s important to note that while cold milk can offer temporary relief, its effects are not long-lasting, and it may not address the underlying causes of heartburn.
Additionally, individual responses may vary, so experimenting with different temperatures and observing personal reactions can help determine what works best for managing heartburn symptoms effectively.
What Milk is Good for Acid Reflux?
Choosing the right type of milk when dealing with acid reflux involves considering its fat content and potential for aggravating symptoms. Low-fat or fat-free milk is generally recommended over whole milk or full-fat dairy products.
These options are less likely to stimulate excessive acid production in the stomach and are easier to digest, which can help alleviate acid reflux symptoms.
Additionally, lactose-free milk or alternatives like almond milk or soy milk can be suitable choices for individuals who are lactose intolerant or prefer non-dairy options.

Lactose-free Milk: Suitable for individuals who are lactose intolerant.
Almond Milk or Soy Milk: Non-dairy alternatives that are gentler on the stomach.
Avoid Whole Milk: Higher fat content can stimulate acid production and worsen symptoms.
Personal Preference: Choosing milk that suits individual tolerance levels and preferences can help manage acid reflux effectively.
What Alleviates Heartburn?
Alleviating heartburn and acid reflux can often be effectively managed through various natural remedies that help soothe the digestive system and reduce discomfort. These remedies focus on neutralizing stomach acid, strengthening the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), and promoting overall digestive health.
Natural Remedies for Acid Reflux:
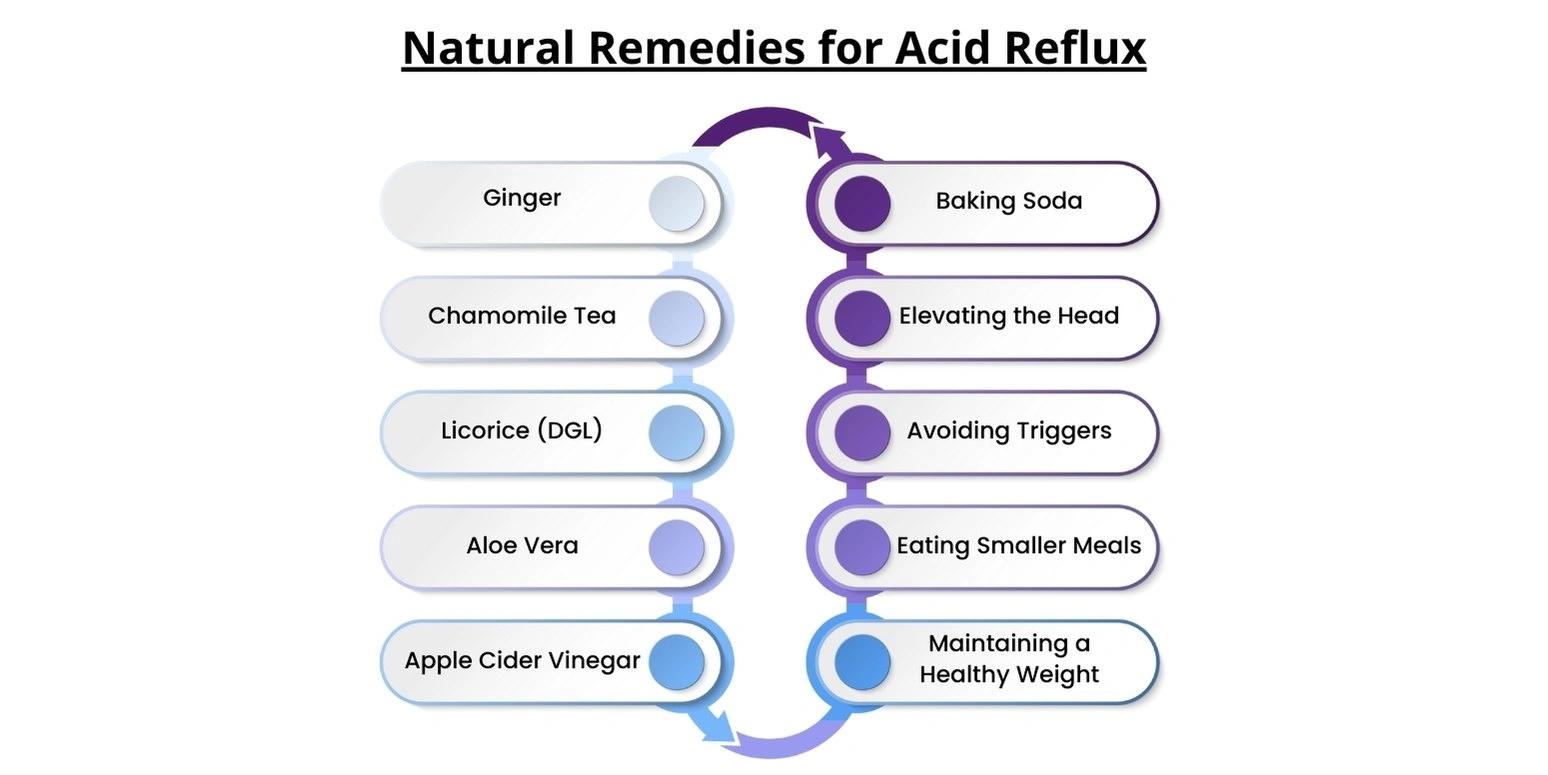
Chamomile Tea: Known for its calming properties, chamomile tea can soothe the digestive tract and reduce inflammation in the stomach and esophagus. Drinking a cup before or after meals may help prevent heartburn.
Licorice (DGL): Deglycyrrhizinated licorice (DGL) is a form of licorice root that has been processed to remove glycyrrhizin, which can raise blood pressure. DGL helps stimulate mucus production in the stomach lining, providing protective relief against acid.
Aloe Vera: Contains anti-inflammatory properties that can help calm the lining of the esophagus. Drinking aloe vera juice, specifically made for internal use, can provide relief from heartburn.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Despite its acidic nature, diluted apple cider vinegar can help balance stomach acid levels. Mix one tablespoon of raw, unfiltered apple cider vinegar in a large glass of water and drink it before meals to aid digestion.
Baking Soda: Baking soda acts as a natural antacid by neutralizing stomach acid. Mix half to one teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of water and drink it to alleviate heartburn symptoms.
Elevating the Head: Sleeping with the head and chest elevated can prevent acid from traveling up the esophagus during the night. Use pillows or a bed wedge to elevate the upper body.
Avoiding Triggers: Certain foods and beverages can trigger heartburn and acid reflux, including spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol. Limiting or avoiding these triggers can help prevent symptoms.
Eating Smaller Meals: Consuming smaller, more frequent meals reduces pressure on the stomach and minimizes the likelihood of acid reflux. Eating slowly and chewing food thoroughly also aids digestion.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can put pressure on the stomach and LES, leading to acid reflux. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can reduce symptoms.
How Do I Stop Indigestion at Night?
Stopping indigestion at night involves adopting habits that promote better digestion and reduce the likelihood of acid reflux while sleeping. Start by avoiding heavy meals or large portions close to bedtime, as these can put pressure on the stomach and increase the risk of reflux.
Opt for lighter, easily digestible dinners and finish eating at least two to three hours before lying down. Elevating the head of your bed or using pillows to raise your upper body can help prevent stomach acid from creeping up into the esophagus during the night. Additionally, steer clear of trigger foods and beverages like spicy dishes, caffeine, and alcohol in the evening.
Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, before bed can also reduce stress, which can exacerbate indigestion. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce the discomfort of nighttime indigestion and promote better sleep quality.
Summary
While milk may provide temporary relief for heartburn and indigestion due to its soothing properties, its long-term effectiveness remains debatable. Some individuals find relief from drinking cold milk, but others may experience worsened symptoms due to its potential to stimulate stomach acid production.
It’s important to consider individual tolerance and consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for managing heartburn and indigestion effectively.

